The Impact of Direct Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C (DAA) on Acute Rejection and Donor Specific Antibody Formation in Kidney Transplant Recipients, Evidence from Surveillance Biopsies
Ziad Zaky1, Leal Herlitz1, Joshua Augustine1.
1Nephrology And Hypertension , Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland , OH, United States
Background: Hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) has historically portended a poor outcome after kidney transplantation. With the recent advent of direct antiviral agents (DAA), there has been a high rate of successful HCV eradication after transplantation. However, data on immunologic injury to the allograft after therapy are lacking.
Methods: We studied 20 HCV+ kidney transplant patients (KT) who underwent DAA treatment with median follow up of 26 mos (range 11-117). We collected data on demographics, DAA regimen, CNI levels, allograft function, donor specific antibodies (DSA), and surveillance &/or for cause allograft biopsies findings.
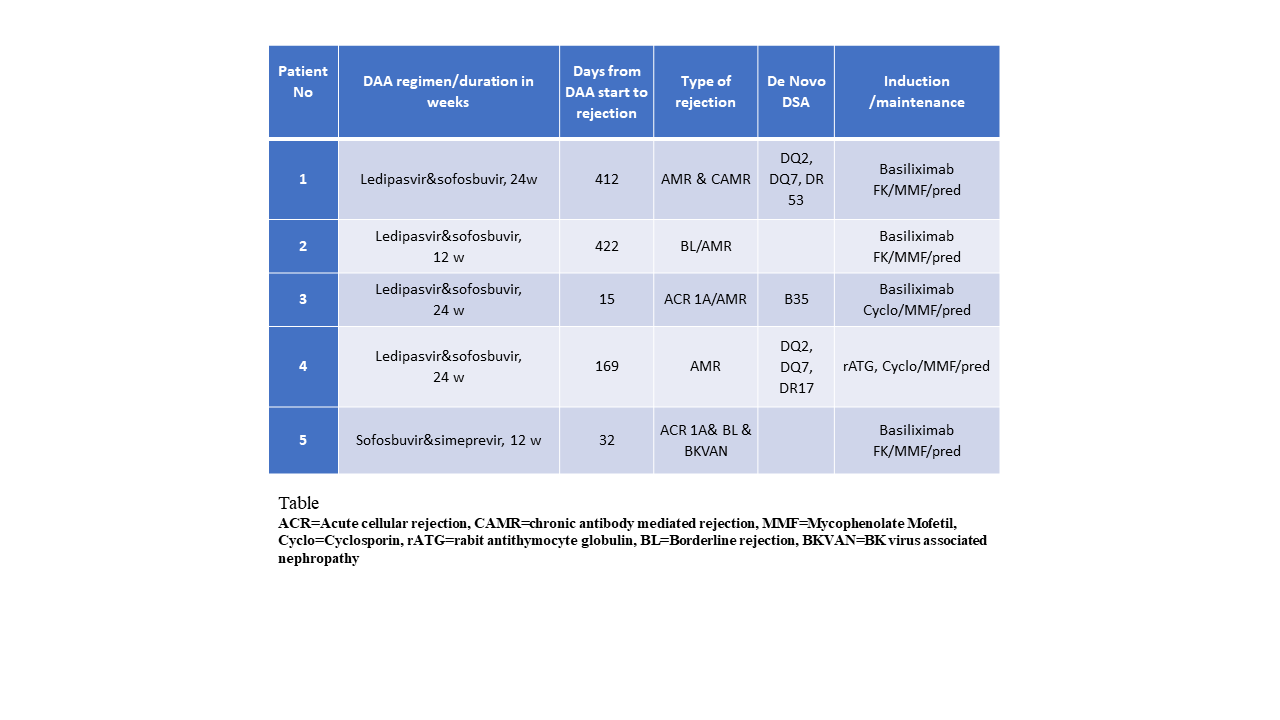
Results: Mean age±SD was 61.9±6.1yo, (18M/2F), 75% were non-Caucasian, all were infected with genotype 1, the DAA regimen was ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (n=19), sofosbuvir and simeprevir (n=1), and 95% achieved sustained virological response. There was no statistical difference between the mean serum creatinine (Cr) and proteinuria (P/Cr ratio) pre DAA treatment and at the last follow up (Cr 1.39 &1.42 mg/dl, p=0.58, P/Cr 0.74-0.91, p=0.64). 11 KT had biopsy proven rejection (pre DAA n=6, post DAA n=5). Mean follow up time from DAA start to last follow up was 21.7 mo±10.1. Of notice all Antibody mediated rejections (AMR) were in the post DAA (table). There was a downtrend in mean Tacrolimus levels (n=18) during DAA with statistical significant difference 2 weeks prior to DAA start and week 12 of DAA treatment (-3.22, p=0.0042) (Figure).
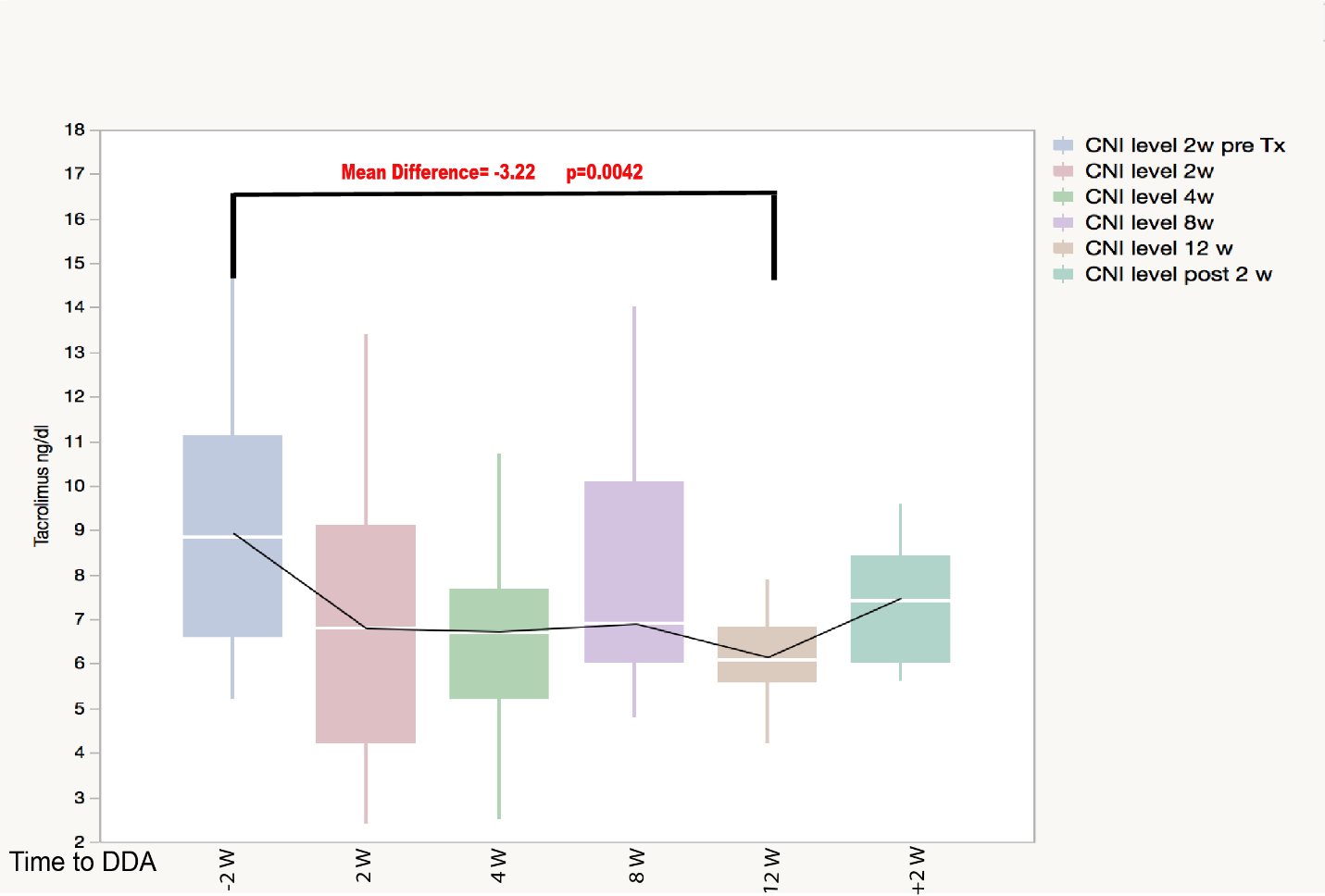
Conclusion: There is a significant decline in mean CNI levels during DAA therapy in KT.In addition, despite relatively stable allograft function in terms of serum creatinine and proteinuria, there is a significant incidence of clinical and subclinical rejection 5/20 (25%) especially AMR 4/5 (80%) detected by protocol and for-cause biopsies.This study highlights the need for close monitoring of immunosuppression, as well as immunologic and histologic surveillance during DAA administration for HCV.